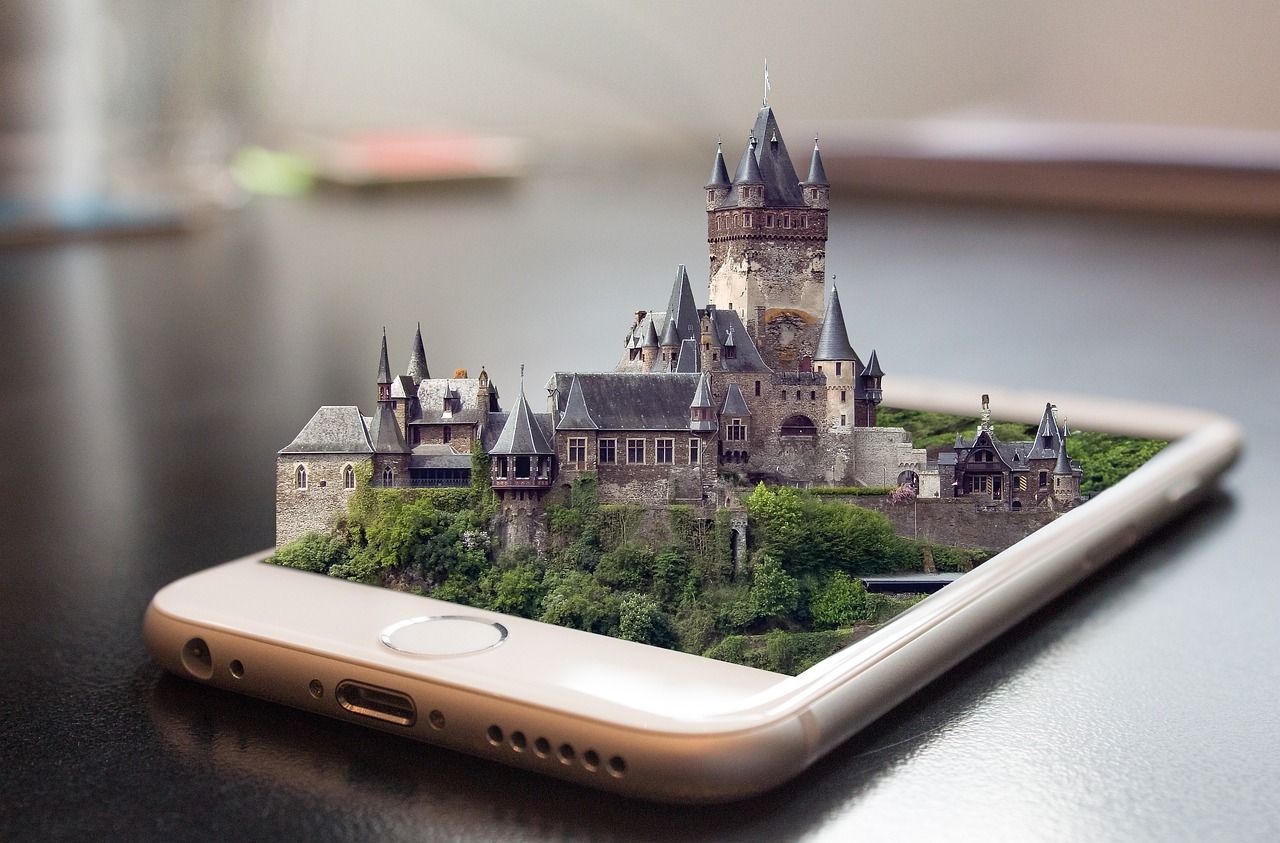
Augmented reality (AR) has been around for decades, but it has only been in recent years that the technology has become mainstream and found practical applications in various industries. But what exactly is augmented reality? Simply put, Augmented Reality is a technology that overlays digital information, such as text, images, or 3D models, onto the real-world environment through a device's camera. It essentially enhances our perception of reality by blending the physical and digital worlds.
The origins of AR can be traced back to the 1960s when Ivan Sutherland, a computer scientist, invented the first head-mounted display system called "The Sword of Damocles." However, it wasn't until the 1990s that the term "augmented reality" was coined by researchers at Boeing. With the advent of powerful mobile devices and advancements in computer vision and machine learning, AR has become more accessible and practical for everyday use.
One of the pioneers of modern AR is Pokémon Go, the wildly popular mobile game that launched in 2016. By leveraging a smartphone's camera and GPS, the game allowed players to catch virtual Pokémon characters overlaid onto the real world. Its success demonstrated the potential of AR and paved the way for wider adoption across various industries.
Augmented Reality on Mobile Devices
Mobile devices have been at the forefront of AR adoption, thanks to their built-in cameras, sensors, and powerful processors. Both iOS and Android operating systems now support AR capabilities, making it easier for developers to create AR apps for a wide range of use cases.
The popularity of mobile AR apps has skyrocketed in recent years, with Google continuously testing and certifying new devices for its ARCore platform. As of late 2020, over 40 smartphone models, including budget-friendly options, were ARCore-compatible. This widespread availability has made AR more accessible to a broader user base.

Photo from Pixabay
So, how does mobile AR work? In simple terms, the device's camera captures data from the real world, such as objects, text, or barcodes. This data is then used to select and overlay relevant digital content onto the camera feed. For example, an AR app could recognize a product on a store shelf and display additional information like reviews, promotions, or nutritional details overlaid onto the physical item.
One of the most well-known examples of mobile AR is, of course, Pokémon Go. By overlaying virtual creatures onto the real-world environment, the game encouraged users to explore their surroundings while catching Pokémon through their smartphone screens.
Augmented Reality-Enabled Shopping Experience
Another area where AR is making a significant impact is the retail industry. Many retailers, including giants like Amazon, Target, and IKEA, have embraced AR to enhance the shopping experience for their customers.
With AR, shoppers can virtually "try on" clothing, accessories, or makeup before making a purchase. Furniture retailers like IKEA allow customers to visualize how a couch or dining table would look in their homes using AR apps. This try-before-you-buy approach not only increases customer satisfaction but also reduces the likelihood of returns and exchanges.
According to recent statistics, 61% of modern shoppers prefer to shop at stores that offer AR experiences, and 46% of retailers are actively exploring AR or VR solutions to stay competitive. Experts predict that the AR market in retail will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 39% from 2021 to 2027, highlighting the increasing importance of this technology in the shopping realm.
By incorporating AR into their marketing campaigns, business processes, and customer service efforts, retailers can increase brand awareness, streamline operations, and provide a more engaging and fun shopping experience for their customers.
Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is another sector where augmented reality is making significant strides. With an estimated market value of $2.4 billion by 2026, AR is being utilized in various medical applications, from surgical training and planning to patient education and diagnostics.
One area where AR is proving particularly useful is in assisting medical professionals with procedures like blood drawing. By mapping out a patient's veins using AR technology, doctors and nurses can accurately locate the best vein for needle insertion, reducing the chances of multiple attempts and discomfort for the patient. Studies have shown that AR can decrease the pain associated with blood drawing by up to 39%.
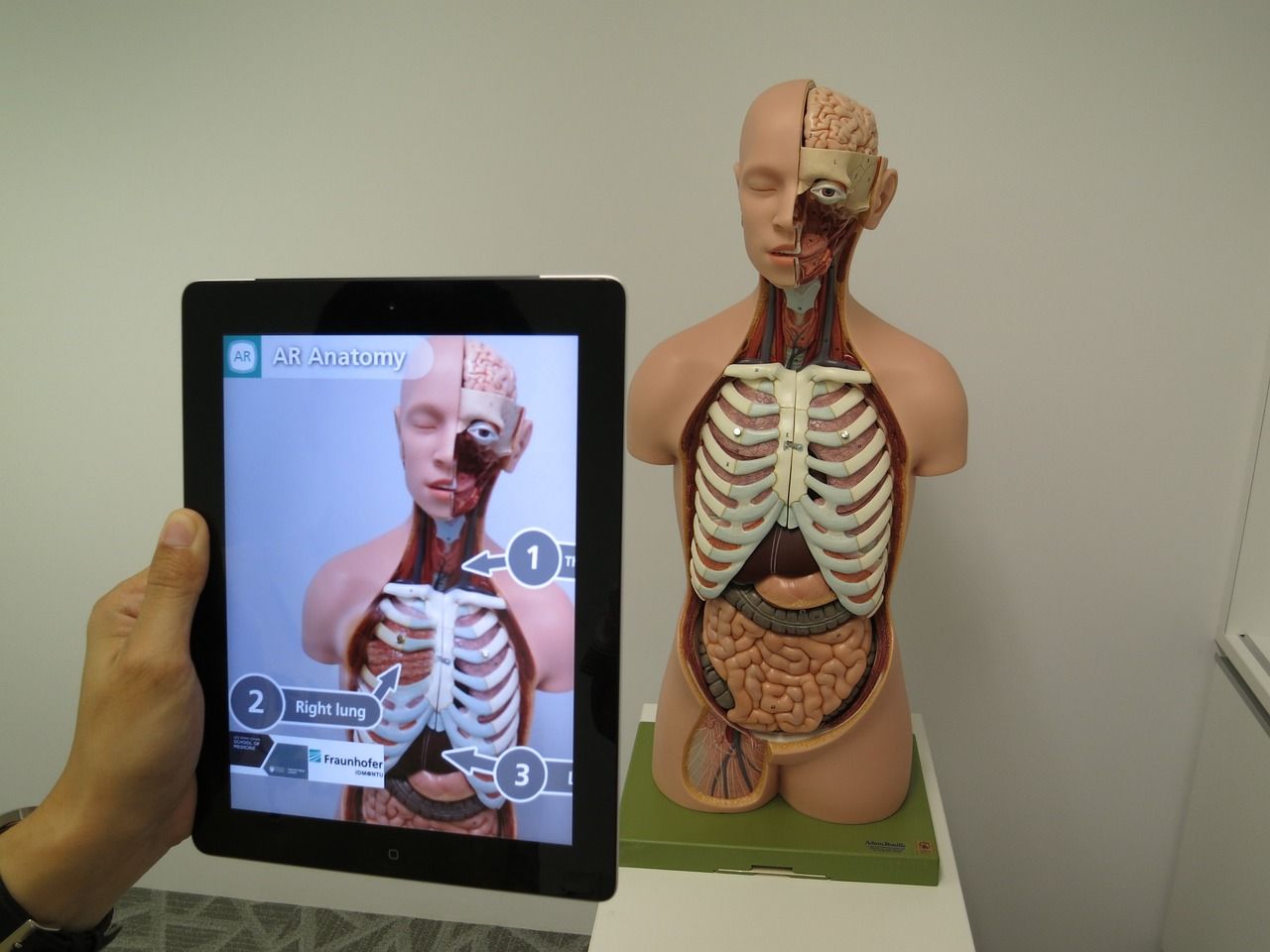
Photo from Pixabay
AR is also being used to enhance patient understanding and education. Doctors can use AR to simplify complex medical terminology and visually explain conditions or procedures to patients, improving communication and comprehension.
During surgical procedures, AR can display patient records, checklists, and walkthroughs of the affected organs directly in the surgeon's field of view, streamlining the process and reducing the risk of errors. Surgeons can also use AR to practice and plan complex procedures before the actual surgery, leading to better preparation and potentially better outcomes.
The Future of Augmented Reality
As technology continues to advance, the applications of augmented reality are expected to grow exponentially. In the retail sector, we can anticipate even more immersive and personalized shopping experiences, with AR allowing customers to virtually try on clothing, accessories, or even makeup shades with pinpoint accuracy.
In healthcare, AR could revolutionize medical training by providing realistic simulations for students and aspiring professionals to practice various procedures in a risk-free environment. Additionally, AR could play a crucial role in telemedicine, enabling remote consultations and diagnosis with the aid of visual aids and overlays.

Photo from Pixabay
The potential applications of AR extend far beyond these industries, with promising use cases in education, tourism, manufacturing, and even entertainment. As AR hardware becomes more sophisticated and affordable, and as the technology becomes more seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, we can expect to see augmented reality transform the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
In conclusion, augmented reality is no longer a futuristic concept; it's a technology that is rapidly becoming integrated into various aspects of our lives. From enhancing our shopping experiences and improving medical procedures to revolutionizing education and entertainment, AR has the potential to bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds in ways we never imagined. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to witness even more innovative and practical applications of augmented reality that will shape the way we live, work, and play.







